Existing methods of treating cervical osteochondrosis aim to reduce symptoms, prevent complications, prevent further damage to the cartilage and bone tissue of the spine, and prevent disability in patients.
Osteochondrosis is a pathological degenerative process of destruction that first captures the intervertebral disc and then the vertebrae themselves.
After the first signs of the disease, it is necessary to treat osteochondrosis of the neck area immediately.
The development mechanism of osteochondrosis
The spine consists of vertebrae and the intervertebral discs that lie between them. In the center of the disc is a gelatinous nucleus pulposus surrounded by a dense annulus fibrosus. The nucleus pulposus is hydrophilic - filled with water and characterized by high elasticity. Provides cushioning and mobility of the spine due to the elastic properties of the disc.
In people over the age of 20, the discs have begun to gradually lose their elasticity. This is due to occlusion of the blood vessels supplying the intervertebral disc, and further blood supply is due to the spread of the adjacent vertebral bodies. In cartilage tissue, on a background of lack of nutrients, the regeneration process slows down - the disc begins to "age". Initially, the nucleus pulposus dehydrates, loses elasticity, and becomes flattened, which increases the load on the annulus fibrosus. Microcracks, tension zones, fractures, delaminations appear in the ring structure.
The degenerated disc protrudes into the spinal canal and stimulates the nerve endings of pain receptors located on the posterior longitudinal ligament.
The pathological process characteristics of cervical osteochondrosis are related to the anatomical structure of the spine: the cervical vertebrae are different in structure and size, the intervertebral joints are tighter, and the muscle structure is underdeveloped. The neck area is permanently loaded with static loads (working in front of the computer), the weaker muscles don't support the head well, and the main load falls on the spine.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in specialist clinics is performed under the supervision of a doctor using a unique technique based on a combination of manual therapy, electrophoresis and photodynamic laser therapy.
The main reasons for the development of osteochondrosis are:
- Congenital or acquired abnormalities of the spine.
- The body's natural aging process.
- Genetic susceptibility.
- Long-term static and dynamic overloading of the spine: forced posture, hypodynamics.
- Passionate about sports that are harmful to the spine: professional wrestling.
- smokes.
- Autoimmune disease in which connective tissue is damaged - collagen disease.
- Malnutrition, mainly carbohydrates and fatty foods, lack of protein, vitamins, trace elements and macro elements.
- Overweight, obese.
- Injuries and diseases of the spine.
Osteochondrosis of the spine - is there such a diagnosis?
In English medicine, this term refers to a completely different group of diseases unrelated to our "native" osteochondrosis. In the International Classification of Diseases—a book that all neurologists should refer to when making a diagnosis—there are titles such as "Spine Osteochondrosis in Adults", "Spine Osteochondrosis in Adolescents", "Spine Osteochondrosis, Indicates "equivalent term".
However, sometimes this diagnosis isn't entirely plausible because doctors can't actually figure out exactly what happened to the patient. Under this term, diseases such as:
- myofascial pain syndrome- Continued spasms in the same muscle.
- Muscle damage.After an injury, the pains start to appear, and they go away on their own after a while.
- otolithiasisA condition in which calcium salt crystals build up in the inner ear. They cause dizziness - sometimes they are mistaken for manifestations of spinal disorders.
- Headache.They are also often associated with degenerative changes in the cervical spine. In fact, they often have other reasons.
Take care of yourself, sign up for a consultation now, and don't delay treatment.
Treatment of spinal osteochondrosis
Standard treatments for disease progression are as follows:
- Anti-inflammatory and pain relievers.Doctors may prescribe Voltaren, Movalis, ibuprofen, and other medicines.
- If the pain is very strong and does not go away- Use of neocaine blockers. A doctor holds a needle and a syringe and injects anesthesia into a special place to block the transmission of painful nerve impulses.
- Physical therapy helps:Drug electrophoresis was performed with neocaine, ultrasound, ultraviolet irradiation, and dual power current.
- If the pain keeps your nerves on edge,Prescribe some medicine to help you calm down.
- to the painful areaApply dry heat.
- To remove the spine,Use different types of traction. The patient can be placed on a special bed with a raised headboard and underarms secured with rings. Underwater traction in the pool is also used.
- doctor may recommendYou go to a chiropractor for an acupuncture session.
- during the deteriorationWear special orthopedic devices that help reduce the load on the muscles and support the spine - corsets, Shats collars.
When an exacerbation passes, you need to take steps to help prevent new exacerbations. Therapeutic exercises and massage help strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Designated physical therapy courses. Suitable for swimming. All treatments for osteochondrosis have contraindications and must be used judiciously, so self-medication is not the best option. Go to the doctor.
Sometimes, despite treatment, the symptoms of the disease continue to worsen and the patient's condition worsens. In this case, the neurologist may raise the question of surgical treatment.

Why go to the doctor as soon as possible? First, "true" osteochondrosis is not a harmless disease. Over time, it can be disabling if left untreated. Second, these symptoms may be caused by the same myofascial pain syndrome - a neurologist will be able to quickly identify the cause of the pain and eliminate it.
Back pain is a symptom that, according to statistics, more than 90% of people experience it at least once in their lifetime. Mostly, it is attributed to osteochondrosis. Not everyone who experiences back pain sees a doctor. Many people self-medicate with medications that are available without a prescription at a pharmacy, folk remedies. Sometimes such "treatments" bring temporary relief - in the meantime, the disease may continue to progress, perhaps with more "twisting" of the back or lower back next time.
An experienced neurologist will be able to properly assess the symptoms of osteochondrosis, understand its cause and prescribe the correct treatment for osteochondrosis.
Pain - the main manifestation of osteochondrosis - with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs and some folk remedies, you can more or less successfully fight for a long time. But that didn't solve the main problem, and the lesions in the spine continued to grow.
Over time, this is fraught with compression of the spinal cord and the arteries supplying it, the development of severe neurological complications: severe impairment of movement and sensitivity to complete loss, impaired control of the bladder, rectum.
Developmental stages of cervical osteochondrosis
During its development, cervical osteochondrosis, as a disease, goes through several stages:
I'm on stage. The initial characteristic is localized pain in the neck, aggravated by turning and tilting the head. There is smooth cervical lordosis and muscle tension. Morphological changes begin with the disc structure: the nucleus pulposus is dry and the annulus fibrosus is ruptured.
Stage two. Neck pain increases with irradiation of the arms and shoulders. Severe headache, weakness, decreased productivity. Destruction of the annulus fibrosus continued, with signs of pathological activity and vertebral instability.
The third phase. Neck pain is intense, persistent, and radiates to the arms and shoulders. Hand muscles weaken and upper extremities become numb. The patient had headache, dizziness, and spatial disorientation. At this stage, the annulus fibrosus is completely destroyed. The gelatinous nucleus pulposus is not fixed and crosses the vertebra into the spinal canal, forming a hernia. The herniation compresses nerves and blood vessels, resulting in impaired circulation to the cervical spine.
Phase IV. This is the final stage of the disease. The cartilage of the intervertebral disc is replaced by connective tissue, and adjacent segments of the spine are involved in the pathological process. The joints grow together and become immobile (stiff). The patient is seriously ill: not only severe pain in the neck, but also severe pain between the arms, chest, and shoulder blades, signs of cerebrovascular accident, and sensitivity disorders. This is a life-threatening condition that can lead to a stroke.
The success of treatment is 90% dependent on the experience and qualifications of the physician.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is based on: patient complaints, characteristic clinical manifestations, disease history, data from neurological and orthopedic examinations of the patient using modern diagnostic methods: radiography, magnetic and computed tomography, and the results of functional tests.
After an accurate diagnosis is made, the doctor decides how to treat the patient's osteochondrosis of the neck and which technique to use in a particular situation.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis is mainly managed symptomatically through conservative approaches, including:
- Medication, including pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, B vitamins.
- Physical therapy methods: electrophoresis, laser therapy.
- Manipulative therapy.
- acupuncture.
- physiotherapy.
Surgical intervention is rarely used when there is a real threat of stroke, paralysis, or invasion of internal organs.
At this stage of medical development, cervical osteochondrosis cannot be completely cured, but it can prevent the further development of the pathological process and stabilize the state of the affected spinal segment.
A comprehensive approach, the sparing nature of the applied treatment allows you to effectively treat even advanced forms of cervical osteochondrosis.
The main methods of modern clinical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Manual therapy and osteopathy. This method of manually impacting problem areas of the spine is designed to restore the normal physiological position of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. During the procedure, the pinching of the spinal nerve roots is removed and the neck muscles are relaxed in the diseased area.
Electrophoresis is a method of delivering drugs directly to the area of the affected spinal segment. Prescribe medications that improve circulation and relieve inflammation and muscle spasms.
Photodynamic light therapy. The method is based on the ability of the photosensitive agent to be activated by laser radiation. Apply a layer of the drug to the skin of the affected area, 10-13 cm deep into the tissue, with anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
The author's three-component technique of manual therapy, electrophoresis, and laser therapy allows you to quickly relieve pain, eliminate swelling of surrounding tissues, improve blood supply to areas of inflammation, and activate the metabolic processes of damaged cartilage tissue in the disc. The goal of treatment is not only to relieve pain and improve the patient's condition, but also to prevent further destruction of the intervertebral disc and destruction of the vertebrae themselves, by acting on various parts of the pathological process.
The techniques used in modern clinics to treat osteochondrosis of the neck have been tested in the best manual therapy centers in Europe and the United States, and they are safe, effective, have few contraindications, and are well tolerated by even elderly patients in groups.
Advice on how to manage cervical osteochondrosis, patients will receive after consulting a neurologist, will depend on the stage of the disease, severity of symptoms, comorbidities, and test results.
Neck osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the neck is a degenerative disease that is actually "premature aging", "wear and tear" of cervical discs, joints, and vertebrae.
Some facts about this disease:
- Osteochondrosis of the neck occurs about the same frequency in men and women.
- Most of the time, people aged 30-60 get sick.
- Often, morbidity occurs with people who have to constantly be in the same position and perform monotonous movements at work.
- The cervical spine has some structural features, so the disease can manifest in many different ways.
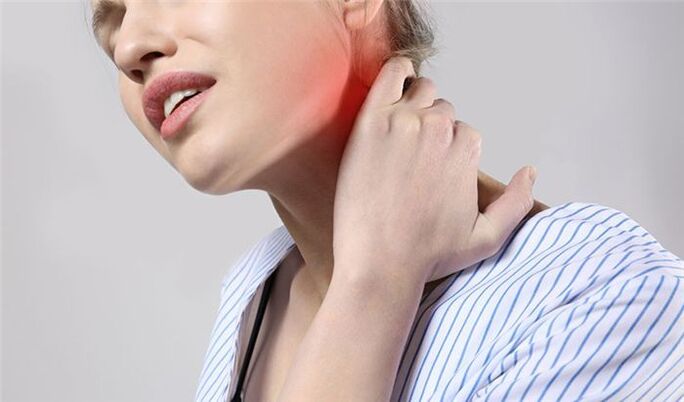
What features of the cervical spine cause symptoms of osteochondrosis?
- There are openings in the lateral processes of the vertebrae - the carotid arteries pass through them on the left and right, supplying blood to the brain.
- In the neck area passes the initial part of the spinal cord - it contains fibers that transmit nerve impulses to various parts of the body, providing movement, sensitivity. If the spinal cord in the neck is compressed, neurological disorders can occur throughout the body.
- This part of the spine is highly mobile and prone to osteochondrosis (although in most cases the disease still occurs in the lumbar region - which is not only mobile but also subject to the most stress).
- In the neck, nerve roots emerge from the intervertebral foramen to form the cervical and brachial plexuses. They are responsible for the movement of neck, arm, shoulder girdle muscles, skin sensitivity, regulation of autonomic function.
- The first vertebra doesn't have a huge front - the body - it's a bony ring that rests on the teeth - the bone grows on the second vertebra. This allows the head to turn left and right.
Neck pain, headache, weakness, and numbness in your hands are symptoms that should lead you to a neurologist. Expert examination and examination with modern equipment will help to understand the cause of the pathology and take the most effective measures.
What happens to the vertebrae in cervical osteochondrosis?
The incomprehensible medical term "degenerative process" refers to the following pathological changes in the cervical spine:
- First, the lesions of osteochondrosis cover the intervertebral discs. They become thinner, reducing the distance between adjacent vertebrae. On their outside, small gaps, microcracks, are formed. Over time, this can lead to a herniated disc.
- Due to disc damage, the stability of the vertebral connection is disturbed.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and intervertebral joints - the development of spondyloarthropathies. It also promotes compression of nerve roots.
- The pathological process extends to the vertebrae themselves. As the function of the intervertebral discs is impaired, their load increases. The spine tries to compensate for this encroachment, and osteophytes -- osteophytes -- develop on the bones.
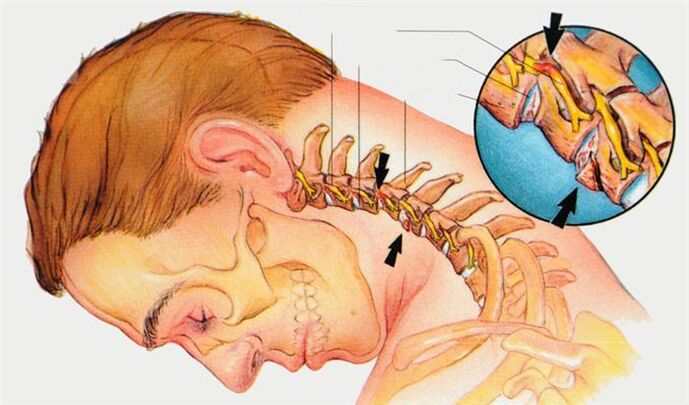
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
During exacerbations of cervical osteochondrosis, traction (the patient is placed on a bed with a raised headboard and the head is held in place with a special ring) is used to unload the intervertebral disc. For the same purpose, you need to wear a Shants collar. To relieve pain, doctors prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe pain that doesn't go away, doctors can perform a blockade: An anesthetic solution is injected into the affected nerve root area. Use of physical therapy: ultrasound therapy, neocaine electrophoresis.
When the condition worsens, the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis includes massage, physical therapy, and physical therapy.
One of the main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis is neck pain. Instead of seeing a doctor, many people facing this condition prefer to treat "rickets" at home. There are at least two good reasons for refusing to self-medicate and to consult a specialist.
First, painkillers and folk methods, while providing temporary pain relief, do not solve the main problem. Pathological changes in the spine continue to grow. Over time, this could have more serious consequences. to the point where surgery may be required.
Second, neck pain doesn’t just happen in osteochondrosis. There are many other reasons. Only a doctor can understand and prescribe the correct treatment.
physiotherapy
The treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is a long processAn integrated approach is required. After you get rid of your main symptoms, you can continue with a variety of physical therapy programs:
- Ultra-high frequency therapy.Exposure to high frequency electromagnetic fields. It is anti-inflammatory, analgesic and also promotes the initiation of the regeneration process.
- Amplify the pulse.Low frequency current is applied to problem areas of the body. Blood vessels dilate, eliminating pain and spasms.
- Electrophoresis and electrophoresis.Use ultrasound and direct current to introduce drugs into deep tissue.
Massage procedures are also widely used and are only possible after eliminating the inflammatory process. Massage promotes muscle relaxation and gets rid of spasms.
Diet - Comprehensive Treatment of Osteochondrosis
With this disease, one has to act in a complex way, so changing your diet is a completely effective treatment. The diet is fairly consistent with the generally accepted understanding of the concept of healthy eating, so try adding the following types of foods to your diet:
- Citrus fruits (in the absence of allergies).
- olive oil.
- Fresh herbs and vegetables.
- mineral water.
- Fish and foods rich in phosphorus, protein, magnesium and calcium.
- Dairy and dairy products.
An excellent aid would be a ready-made vitamin complex, which can be found in a large variety in pharmacy chains. Remember, all medicines should only be taken as prescribed by your doctor.
Which symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis should bring you to see a doctor?
The main symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is pain. It can occur in different places, depending on the level of localization of the pathological process: neck, shoulder girdle, arm, heart area. Essentially, the pain sensation is dull, possibly searing, painful.
Other manifestations of the disease:
- Headache, dizziness, "fly in front of eyes", noise, tinnitus.
- Neck, shoulder girdle, arm muscle weakness.
- Violation of skin sensitivity.
- Frozen shoulder: neck pain transmitted to the arm, difficulty in arm abduction more than 90°, weakness and atrophy of the shoulder girdle muscles.
- Shoulder-hand syndrome: shoulder and hand pain, swollen and stiff fingers, weakness and atrophy of hand muscles.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. Bone growths develop on the vertebrae, compressing the nerves, causing reflex spasms of the vertebral arteries that supply blood to the brain. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are accompanied by a persistent headache that starts at the back of the head, spreads to the temples, to the top of the head, nausea, head noises, ringing in the ears, and flashing bright spots in front of the eyes.
- Anterior scalene syndrome. There's an anterior scalene and a middle scalene muscle in the neck -- they're just around the corner, and there's a small space between them where the nerves and blood vessels run through. With cervical osteochondrosis, the anterior scalene muscles become tense and squeeze them, causing symptoms such as pain on the inner surfaces of the forearm, shoulder, and fingers. Sometimes the pain radiates to the back of the head. The skin of the hands may become cold, pale, and numb.
- Epicondylitis syndrome. On the lower part of the shoulder, on either side of the elbow joint, there are bony protrusions called the epicondyles. For epicondylitis syndrome caused by cervical osteochondrosis, they can be painful, which increases with pressure. Other symptoms may also occur: neck pain, pain when pressing certain parts of the cervical spine area.
If both parts of the spine are affected at the same time, with cervicosternal osteochondrosis, symptoms may include pain between the shoulder blades in the heart area.
With osteochondrosis, the risk of intervertebral hernia and stroke increases. If you experience any of the above symptoms, see your doctor.
in conclusion
Now you know how to treat cervical osteochondrosis without surgical intervention. Surgery is the ultimate treatment when the disease has spread and there is no other way out. However, you have the ability to do so lest your health reach this state.